New insights into the architecture of the islet of Langerhans: a focused cross-species assessment. Many studies on human islet cells rely on the legacy of rodent-based investigations. Since islet physiology and pathology may differ between rodents and humans, the current knowledge of interspecies islet cell cytoarchitecture and its potential impact on islet function is reviewed …
PI3K-C2α Knockdown Results in Rerouting of Insulin Signaling and Pancreatic Beta Cell Proliferation. Insulin resistance is a syndrome that affects multiple insulin target tissues, each having different biological functions regulated by insulin. A remaining question is how an insulin target cell/tissue can be insulin resistant in one biological function and insulin sensitive in another at …
Apolipoprotein a1 increases mitochondrial biogenesis through AMP-activated protein kinase. A study presented in the September issue of Cellular Signalling, suggests that apolipoprotein a1 can alleviate obesity related metabolic disease by inducing AMPK dependent mitochondrial biogenesis. Read more: Apolipoprotein a1 increases mitochondrial biogenesis through AMP-activated protein kinase. Parkyong Song, Yonghoon Kwon, Kyungmoo Yea, Hyo-Youl Moon, …
Agonistic aptamer to the insulin receptor leads to biased signaling and functional selectivity through allosteric modulation. In this study IR-A48 is presented as a biased agonist able to selectively induce the metabolic activity of insulin receptors through allosteric binding. This is the first study to show that aptamer–protein interactions can not only differentially modulate receptor …
The pancreatic beta-cell in deadly encounter with apolipoprotein CIII A publication in Cell Cycle describes studies which demonstrate that preventing insulin resistance at the islet level is crucial to maintain beta-cell function and survival in diabetes. Tests in a T2DM mouse model were performed using the Biocrine InSight in vivo technology. Targeting the local islet …
Glucose intolerance and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in the anorectic anx/anx mouse. Previous studies have revealed inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in the hypothalamus of an animal model for anorexia. Also, increased incidence of eating disorders has been observed in diabetic individuals. In the American Journal of Physiology – Endocrinology and Metabolism, data from studies is presented which …
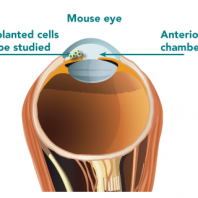
Pancreatic Islet Survival and Engraftment Is Promoted by Culture on Functionalized Spider Silk Matrices. General transplantations of pancreatic islets as treatment for insulin-dependent diabetes have so far been of limited success. The challenges of providing viable islets in large quantities for transplantation have proven to be extensive. In this study presented in PLOS ONE, mouse …
Apolipoprotein CIII links islet insulin resistance to β-cell failure in diabetes In a study published in the May 2015 issue of PNAS, it was demonstrated that apolipoprotein CIII (apoCIII) can serve as a link between insulin resistance and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Preventing insulin resistance at the islet level is thus crucial …
Pancreatic NMDA receptors as possible drug targets. In contrast to NMDA receptors in the nervous system, the role of NMDA receptors in pancreatic islets and the insulin-secreting beta cells is less known. Data presented in the April issue of Nature Medicine bring new understanding of the cell processes involved in type 2 diabetes mellitus and …
Proteomic Analysis reveals involvement of the FPR2 pathway in insulin resistance Elevated levels of the free fatty acid palmitate are found in the plasma of obese patients and induce insulin resistance. In a study presented in the April issue of Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, the skeletal muscle secretome in response to palmitate-induced insulin resistance was …