The pancreatic beta-cell in deadly encounter with apolipoprotein CIII A publication in Cell Cycle describes studies which demonstrate that preventing insulin resistance at the islet level is crucial to maintain beta-cell function and survival in diabetes. Tests in a T2DM mouse model were performed using the Biocrine InSight in vivo technology. Targeting the local islet …
Glucose intolerance and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in the anorectic anx/anx mouse. Previous studies have revealed inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in the hypothalamus of an animal model for anorexia. Also, increased incidence of eating disorders has been observed in diabetic individuals. In the American Journal of Physiology – Endocrinology and Metabolism, data from studies is presented which …
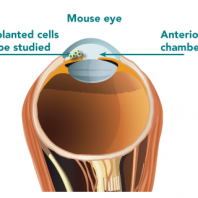
Pancreatic Islet Survival and Engraftment Is Promoted by Culture on Functionalized Spider Silk Matrices. General transplantations of pancreatic islets as treatment for insulin-dependent diabetes have so far been of limited success. The challenges of providing viable islets in large quantities for transplantation have proven to be extensive. In this study presented in PLOS ONE, mouse …
Apolipoprotein CIII links islet insulin resistance to β-cell failure in diabetes In a study published in the May 2015 issue of PNAS, it was demonstrated that apolipoprotein CIII (apoCIII) can serve as a link between insulin resistance and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Preventing insulin resistance at the islet level is thus crucial …
Pancreatic NMDA receptors as possible drug targets. In contrast to NMDA receptors in the nervous system, the role of NMDA receptors in pancreatic islets and the insulin-secreting beta cells is less known. Data presented in the April issue of Nature Medicine bring new understanding of the cell processes involved in type 2 diabetes mellitus and …
Proteomic Analysis reveals involvement of the FPR2 pathway in insulin resistance Elevated levels of the free fatty acid palmitate are found in the plasma of obese patients and induce insulin resistance. In a study presented in the April issue of Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, the skeletal muscle secretome in response to palmitate-induced insulin resistance was …
Voltage-gated CaV channels as potential targets for anti-diabetes therapy The voltage-gated Ca(2+) (CaV) channel acts as a key player in β cell physiology and pathophysiology. β cell CaV channels undergo hyperactivation subsequent to exposure to type 1 diabetic (T1D) serum resulting in Ca(2+)-triggered β cell apoptosis. In the March 2015 issue of Cellular and Molecular …
Regulation of glucose homeostasis using radiogenetics and magnetogenetics in mice Endogenous expression of tailored nanoparticles in cells followed by application of low-frequency radio waves or a magnetic field can be used to noninvasively modulate gene expression. This approach successfully induces insulin transgene expression in diabetic mice. Read more: Regulation of glucose homeostasis using radiogenetics and …
The results from new findings about the molecular mechanisms behind the age-dependent deterioration in β-cell function have been published in Advances in Biological Regulation (formerly Advances in Enzyme Regulation); a journal reporting cutting edge scientific progress on regulation at the molecular level. Defects in pancreatic β-cell function and survival are key components in type 2 diabetes. …
Young capillary vessels rejuvenate aged pancreatic islets. A recent study published in the journal PNAS shows that young capillary vessels rejuvenate aged pancreatic islets. This finding challenges the common view that pancreatic beta-cells become inefficient with age. The reduction of insulin production within the cells may instead be affected by systemic aging factors. Read more: Press release …